|
|
| Tips ‘n’ Tricks |
| |
SuperClass without entering into constructor
of SubClass. Here also the instance variables
of SuperClass are initialized and then super
class’s constructor is called then control
comes back to call the constructor of
SubClass.
SubClass.java:
This example demonstrates the
execution order of a java program.
class SuperClass {
private String supVar1=staticPrintMethod
(“\”SuperClass.supVar1\” initialized”);
public int supVar2;
superClass()
{
System.out.println(“In \”SuperClass\”
constructor.”);
supVar1=”java”;
supVar2=10;
System.out.println(“supVar1 = “ + supVar1
+ “, supVar2 = “ + supVar2);
}
private String staticVarInSuperClass =
staticPrintMethod(“static
\”SuperClass.staticVarInSuperClass\”
initialized”);
static String staticPrintMethod(String str) {
System.out.println(str);
return “success”;
}}
public class SubClass extends SuperClass {
private String subVar1 =
staticPrintMethod(“\”SubClass.subVar1\”
initialized”);
public SubClass() {
System.out.println(“In \”SubClass\”
constructor.”);
System.out.println(“subVar1 = “ +
subVar1);
}
private static String staticVarInSubClass =
staticPrintMethod(“static
\”SubClass.staticVarInSubClass\”
initialized”);
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(“In main() method.”);
SubClass b = new SubClass();
}
}
|
|
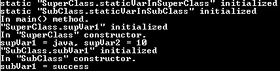
Compile and Run:
C:\JavaJazzup>javac SubClass.java
C:\JavaJazzup>java SubClass
Output:
|
|
Sept 2007 | Java Jazz Up | 75 |
|
| |
Pages:
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23,
24,
25,
26,
27,
28,
29,
30,
31,
32,
33,
34,
35,
36,
37,
38,
39,
40,
41,
42,
43,
44,
45,
46,
47,
48,
49,
50,
51,
52,
53 ,
54,
55,
56,
57,
58,
59,
60,
61,
62,
63 ,
64,
65 ,
66 ,
67 ,
68 ,
69 ,
70,
71,
72,
73,
74,
75,
76,
77,
78,
79, Download PDF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| |
|