|
|
| Tips ‘n’ Tricks |
| |
EnvironmentInformation.java:
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class EnvironmentInformation{
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println(“\n”+”You are working
with
\””+System.getProperty(“os.name”)+
”\”
Operating System “);
System.out.println(“and using jdk version :
\””+System.getProperty(“java.version”)+
”\”\n”);
Map map = System.getenv();
Set keys = map.keySet();
Iterator iterator = keys.iterator();
System.out.println(“List of all environment
variable names and their values :”+”\n”);
System.out.println(“Variable Name
Variable Values”);
System.out.println(“———————\t\t———
————————”);
while (iterator.hasNext())
{
String key = (String) iterator.next();
String value = (String) map.get(key);
System.out.println(key + “ “ +
value);
}
}
}
Compile and Run:
C:\JavaJazzup>javac
EnvironmentInformation.java
C:\JavaJazzup> java EnvironmentInformation
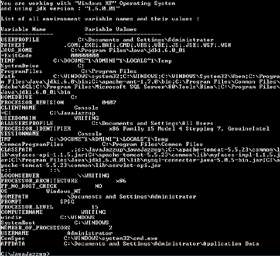
Output:
Above program shows environment
variables as it is shown in the figure below.
|
|
Are you really confident about the execution
flow of a java program?
Sometimes, even a simple java program, can
make you confused about the flow of
initialization of variables and flow of program.
If you are clear with the concept of “static” keyword and flow of constructor calling
(constructor chainging) then the program
below is simple to understand. The compiler
combines multiple static initializer blocks into
a single initialization procedure (which is
executed one time only when the class is
loaded) so the order of execution of program
code will not necessarily be the same as the
order in which the code appears in the
program i.e. non-static code can separate
multiple static initializer blocks. The static
initializer blocks are executed in the order in
which they appear in the code, regardless of
the other code that may separate them. This
causes the program to be a little difficult to
understand.
In the program below first static variables
are initialized. Then main method is called
which calls the SubClass constructor. Here constructor chaining is applied in which every
constructor calls its super class constructor.
So before entering into constructor of
SubClass, its instance variables are initialized.
Now, control goes to call the constructor of
|
|
Sept 2007 | Java Jazz Up | 74 |
|
| |
Pages:
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23,
24,
25,
26,
27,
28,
29,
30,
31,
32,
33,
34,
35,
36,
37,
38,
39,
40,
41,
42,
43,
44,
45,
46,
47,
48,
49,
50,
51,
52,
53 ,
54,
55,
56,
57,
58,
59,
60,
61,
62,
63 ,
64,
65 ,
66 ,
67 ,
68 ,
69 ,
70,
71,
72,
73,
74,
75,
76,
77,
78,
79, Download PDF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| |
|