|
|
| Working with Entity bean using JPA |
|
Managing an Entity Instance’s Life Cycle:
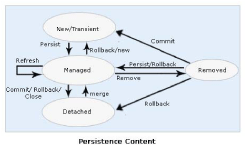
You manage entity instances by invoking
operations on the entity by means of an
EntityManager instance. Entity instances are in
one of four states: new, managed, detached,
or removed.
New entity instances have no persistent
identity and are not yet associated with a
persistence context.
Managed entity instances have a persistent
identity and are associated with a persistence
context.
Detached entity instances have a persistent
identify and are not currently associated with a
persistence context.
Removed entity instances have a persistent
identity, are associated with a persistent
context, and are scheduled for removal from
the data store.
In this part of Enterprise Session Beans, you
will learn how to develop, deploy, and run a
simple JPA application named book using
stateless session bean. The purpose of ‘book’
is to perform the persistence operations such
as Add record and getting information to or
from the database.
The ‘book’ application consists of two enterprise
beans, first is BookBank that defines the Table
name and Primary key in the database, and
second one is BookCatalogBean that
performs the Persistence Object Relational
Mapping.
|
|
There are following steps that you have to
follow to develop a ‘book’ JEE application.
1 Create Remote business interface:
BookCatalogInterface
2 Implement the Annotated Session
Bean: BookCatalogBean
3 Create the Entity bean: BookBank
4 Create the web client: WebClient
5 Deploy book on the server.
6 Run web client on the web browser.
A UML diagram of this application using
JPA can be seen as:
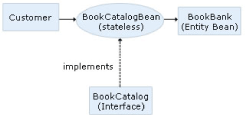
Create Remote Business Interface
To implement a session bean, we first determine
the interface that it exposes. In the Book
application, this is a simple Java interface
declaring all business methods.
package entity.library;
import javax.ejb.Remote;
import java.util.Collection;
@Remote
public interface BookCatalogInterface {
public void addBook(String title, String
author, double price);
public Collection <BookBank>
getAllBooks();
}
II. Implement the annotated session
bean
The EJB3 container creates instances of the
session bean based on the implementation
classes. The application itself never creates
session bean instances. It simply asks the |
|
|
Feb 2008 | Java Jazz Up | 9 |
| |
|
| |
| View All Topics |
| All Pages of this Issue |
Pages:
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23,
24,
25,
26,
27,
28,
29,
30,
31,
32,
33,
34,
35,
36,
37,
38,
39,
40,
41,
42,
43,
44,
45,
46,
47,
48,
49,
50,
51,
52,
53 ,
54,
55,
56,
57,
58,
59,
60,
61,
62,
63 ,
64,
65 ,
66 ,
67 ,
68 ,
69 ,
70 ,
71 ,
72 ,
Download PDF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| |
|