|
|
Working with Entity bean using JPA |
|
Working with Entity bean using JPA API
In the previous issue of Java Jazz Up you
have learnt how a Stateless Bean is developed
in EJB 3. Now you will learn how an Entity Bean
is developed to interact with the Database using
JPA API.
Entity:
An entity defines a table (consisting of rows
and columns) in a relational database. An entity
refers to a logical collection of data that can be
stored or retrieved from that entity. For
example, in a banking application, Customer
and BankAccount can be treated as entities.
Customer name, customer address etc can be
logically grouped together for representing a
Customer entity. Similarly account number, total
balance etc may be logically grouped under
BankAccount entity.
Mapping with EJB3/JPA Annotations:
The EJB 3.0 entity beans are used to model
and access relational database tables. It is a
completely POJO-based persistence framework
with annotations that specify how the object
should be stored in the database. The EJB 3.0
container does the mapping from the objects
to relational database tables automatically and
transparently. Their mappings are defined
through JDK 5.0 annotations (an XML descriptor
syntax for overriding is defined in the EJB3
specification).
Annotations can be split in two categories,
the logical mapping annotations which allows
programmer to describe the object model, the
class associations, etc. and the physical
mapping annotations which describes the
physical schema, tables, columns, indexes, etc.
The combination of annotations from both
categories makes a JPA-based application. Now,
the Java developer no longer needs to worry
about for the implementation of home
interfaces and the details of the database table
schema, database connection management, and
specific database access APIs.
|
|
Introduction to Java Persistence API
(JPA)
Java Persistence API is a lightweight
framework based on POJO for object-relational
mapping. It is the standard API added in Java
EE 5 platform and used for the management of
the persistent data and object/relational
mapping. Persistence that deals with storing
and retrieving of application data can now be
programmed with Java Persistence API starting
from EJB 3.0. Every application server
compatible with Java EE 5 supports the Java
Persistent APIs.
Java language metadata annotations and/or
XML deployment descriptor is used for the
mapping between Java objects and a relational
database.
The Java Persistence API contains the following
areas:
• Java Persistence API
• O-R mapping metadata
• The query language
Here we are describing EJB3-JPA by using the
simple domain object model by an example.
Working process of an EJB application using
JPA:
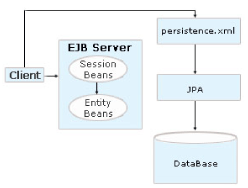
While developing an enterprise application,
first design the domain object model required |
|
|
Feb 2008 | Java Jazz Up | 7 |
| |
|
| |
| View All Topics |
| All Pages of this Issue |
Pages:
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23,
24,
25,
26,
27,
28,
29,
30,
31,
32,
33,
34,
35,
36,
37,
38,
39,
40,
41,
42,
43,
44,
45,
46,
47,
48,
49,
50,
51,
52,
53 ,
54,
55,
56,
57,
58,
59,
60,
61,
62,
63 ,
64,
65 ,
66 ,
67 ,
68 ,
69 ,
70 ,
71 ,
72 ,
Download PDF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| |
|