|
|
| XML Schema |
|
|
Let’s briefly discuss the concept of XML
Namespaces
XML Namespaces provide a mechanism to avoid
element’s name conflicts.
Name Conflicts: Since element names in XML
are not predefined, chances for frequency to
meet name conflict increases when two different
documents use the same element names.
We solve the Name Conflicts using a Prefix
with a element name: By using a prefix, we
can create two different types of elements.
Instead of using only refixes, we add an xmlns
attribute to the conflict causing tags to give
the prefix a qualified name.
The XML Namespace (xmlns) Attribute: The
XML namespace attribute is placed in the start
tag of an element and has the following syntax:
xmlns:namespace-prefix=”namespaceURI”
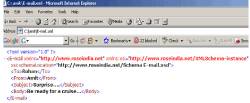
Example 1(taken from E-mail.xml):
<E-mail
xmlns=”http://www.roseindia.net”
xmlns:xsi=”http://www.w3.org/2001/
XMLSchema”
xsi:schemaLocation=”http://www.roseindia.net/
Schema” E-mail.xsd”>
Example 2(taken from E-mail.xsd ):
<xs:schema
xmlns:xs=”http://www.w3.org/2001/
XMLSchema"
targetNamespace=”http://www.roseindia.net”
xmlns=”http://www.roseindia.net”
elementFormDefault=”qualified”>
|
|
When a namespace is defined in the start tag
of an element, all child elements with the same
prefix are associated with the same namespace.
In E-mail.xsd “xs” is the defined namespace in
the start tag. So it prefixes all the child
elements with xs eg...
<xs:element name=”E-mail”>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name=”To” type=”xs:string”/>
<xs:element name=”From” type=”xs:string”/>
<xs:element name=”Subject” type=”xs:string”/ >
<xs:element name=”Body” type=”xs:string”/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
Note that the address used to identify the
namespace is not used by the parser to look
up information. The only purpose is to give the
namespace a unique name. However, very often
companies use the namespace as a pointer to
a real Web page containing information about
the namespace.
Here a Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) is a
string of characters, which identifies an Internet
Resource.
Default Namespaces: Defining a default
namespace for an element saves us from using
prefixes in all the child elements. It has the
following syntax:
xmlns=”namespaceURI” We have not included prefixes in all the child
element tags (To, From, Subject, Body) in our
following example:
<?xml version=”1.0"?>
<E-mail
xmlns=”http://www.roseindia.net”
xmlns:xsi=”http://www.w3.org/2001/
XMLSchema-instance”
x s i : s c h e m a L o c a t i o n = ” h t t p : / /
www.roseindia.net/Schema E-mail.xsd”> |
|
|
Feb 2008 | Java Jazz Up | 18 |
| |
|
| |
| View All Topics |
| All Pages of this Issue |
Pages:
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23,
24,
25,
26,
27,
28,
29,
30,
31,
32,
33,
34,
35,
36,
37,
38,
39,
40,
41,
42,
43,
44,
45,
46,
47,
48,
49,
50,
51,
52,
53 ,
54,
55,
56,
57,
58,
59,
60,
61,
62,
63 ,
64,
65 ,
66 ,
67 ,
68 ,
69 ,
70 ,
71 ,
72 ,
Download PDF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| |
|