|
|
| Introduction to XSL |
The following figure shows the working
process of XSLT:
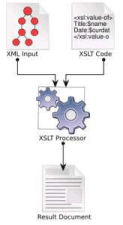
XSLT Processors
The job of an XSLT processor is to apply an
XSLT stylesheet to an XML source document
and produce a result document, (for example
HTML document). There are several XSLT
processors, but a few good one (Open sources),
such as MSXML4, Saxon, and Xalan, XT, Oracle.
Most of them can be downloaded free from Web
sites.
Apache’s Xalan XSLT engine
Xalan is the Apache XML Project’s XSLT engine.
This processor is available at http://
xml.apache.org/xalan/. We will concentrate on
using this engine for transformation our XML
document that we have developed and want to
transform it into output document in the HTML
format.
Once the Xalan.zip or .gzip file is downloaded,
unpack it and add these files to your
CLASSPATH. These files include the .jar file for |
|
the Xerces parser, and the .jar file for the Xalan
stylesheet engine itself. The .jar files are named
xercesImpl.jar, and xalan.jar.
Working with XSLT APIs
XSLT consist of three components that
transform an XML document into the required
format. These components are:
- An instance of the TransformerFactory
- An instance of the Transformer
- The predefined transformation
instruction
TransformerFactory is an abstract class used
to create an instance of the Transformer class
that is responsible for transforming a source
object to a result object.
The process of XML transformation starts when
you create an instance of the
TransformerFactory class. An instance of the Transformer class is then created using the
instance of the TransformerFactory class. This
instance of the Transformer class uses the XML
document as a source object and optionally
uses the predefined instructions required for
transformation to generate the formatted
output as a result object. You can create the
source XML document using SAX, DOM, or an
input stream. The result object of the
transformation process is in the form of a SAX
event handler, DOM, or an output stream.
During transformation process, the original
document is not changed; rather, a new
document is created based on the content of
an existing one. The new document may be
serialized (output) by the processor in standard
XML syntax or in another format, such as HTML
or plain text.
The following figure shows the working
process of XSLT APIs:

|
|
Mar
2008 | Java Jazz Up |14 |
| |
|
| |
| View All Topics |
| All Pages of this Issue |
Pages:
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23,
24,
25,
26,
27,
28,
29,
30,
31,
32,
33,
34,
35,
36,
37,
38,
39,
40,
41,
42,
43,
44,
45,
46,
47,
48,
49,
50,
51,
52,
53 ,
54,
55,
56,
57,
58,
59,
Download PDF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| |
|